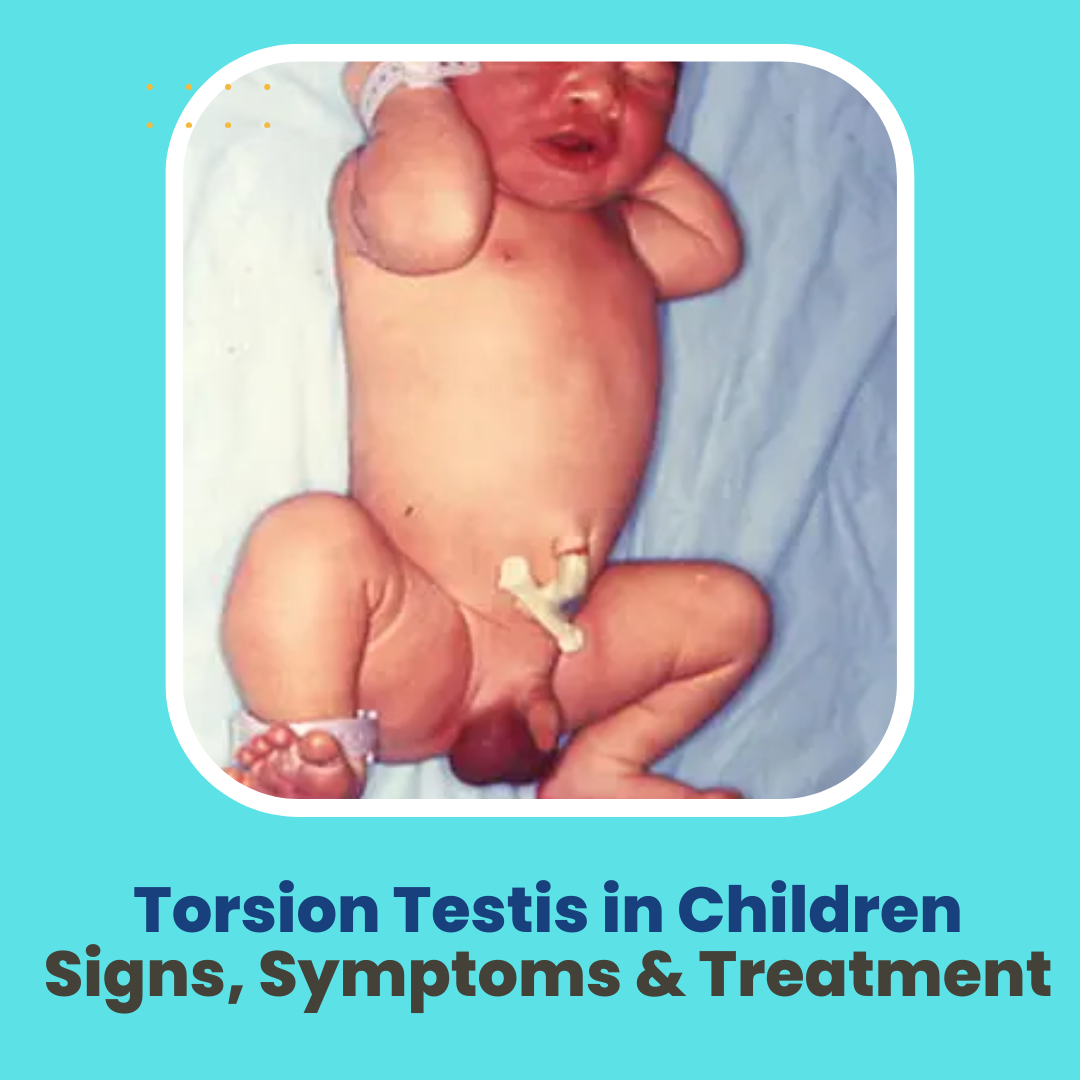
Torsion of the testis is a pediatric surgical emergency that occurs when the testicle rotates, cutting off its blood supply. It requires immediate medical attention to prevent permanent damage to the testicle. Torsion can occur at any age, but it is most commonly seen in pre-adolescent boys. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent permanent damage to the testicle. Torsion testis in Children is a urological emergency that requires immediate medical attention.
Understanding Torsion Testis
Torsion of the testis occurs when the spermatic cord, which provides blood flow to the testicle, twists. This twist can block the blood vessels, leading to ischemia (lack of blood supply) and testicular damage.
Signs and Symptoms of Torsion Testis in Children
Torsion testis presents with specific signs and symptoms that should raise concern for parents and healthcare providers. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Sudden and Severe scrotal or groin Pain: One of the primary symptoms of the torsion testis is sudden and severe pain in the affected testicle. The pain may be accompanied by swelling and tenderness.
- Abdominal Pain: Children with torsion testis may experience abdominal pain, which can sometimes be mistaken for other conditions such as appendicitis.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Due to the intensity of pain, children with torsion testis may experience nausea and vomiting.
- Abnormal Testicular Position: In some cases, the affected testicle may be positioned higher than usual or may be positioned horizontally rather than vertically.
Treatment Options
Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to salvage the affected testicle. The following treatment approaches may be considered:
- Manual Detorsion
If the diagnosis is made early and the blood flow is not severely compromised, the testicle can sometimes be manually detorsed. This procedure involves carefully rotating the testicle back into its normal position to restore blood flow. However, manual detorsion is a temporary measure and should be followed by definitive surgical treatment to prevent a recurrence.
- Surgery
Surgical intervention is typically required to permanently fix the testicle and prevent future episodes of torsion.
- Orchidopexy
Orchidopexy is a surgical procedure that involves fixing the testicle in its proper position to prevent torsion. This procedure is often performed on the healthy Testis during the same surgical intervention used to destrose the testicle. This is to prevent torsion of the healthy Testis in the future.
- Removal of Nonviable Testicle
In cases where the blood supply to the testicle has been compromised for an extended period, the testicle may become nonviable. In such cases, surgical removal of the affected testicle may be necessary.
Conclusion
Testicular torsion is an emergency that requires immediate pediatric surgical treatment. It is important to recognize the signs and symptoms of torsion testis in children, such as sudden and severe testicular pain, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and changes in testicular position. Prompt diagnosis and surgical intervention are crucial to restore blood flow to the affected testicle and prevent permanent damage. Timely treatment can help preserve testicular function and ensure the best possible outcome for your child’s urological health Consult Dr. Geeta Kekre for the best treatment.
About Dr. Geeta Kekre
Dr. Geeta Kekre is a Paediatric Surgeon in Pune She is a specialist in pediatric minimal access surgery including robotic surgery as well as reconstructive pediatric urology. After ten years in Mumbai, Dr. Kekre returned to her hometown bringing with her a passion for the surgical care of children and a distinct set of skills in the areas of pediatric minimal access surgery, pediatric endourology, fetal hydronephrosis and antenatal parental counseling, pediatric incontinence, and voiding dysfunction. Her focus is on tailoring surgical therapy to allow her patients to have as active and fun a childhood as possible while delivering the best achievable medical outcomes.